Concentration measurement in acids
The concentration measurement in acids is an essential part of many chemical and industrial processes. The concentration of an acid in a solution is determined, which is of great importance for understanding its chemical properties and reactions.
The most common acids used in chemistry include: Hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), nitric acid (HNO₃), acetic acid (CH₃COOH) etc.
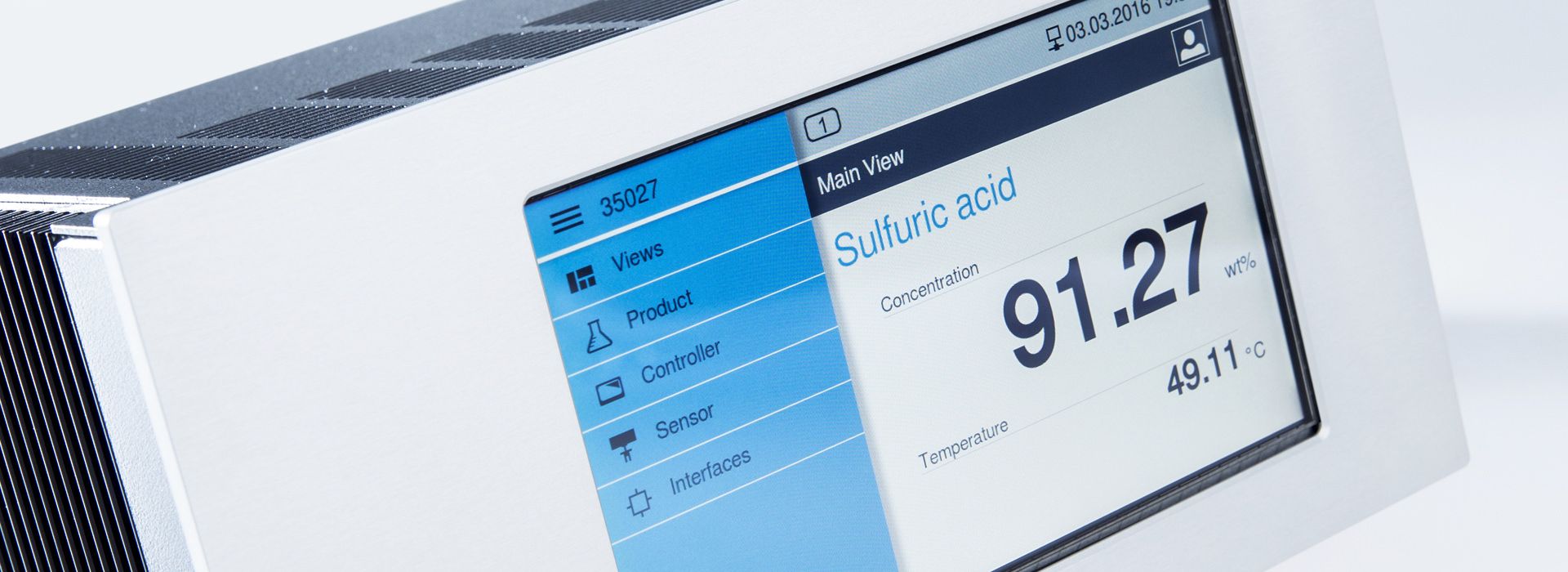
Concentration measurements with LiquiSonic® Measuring devices
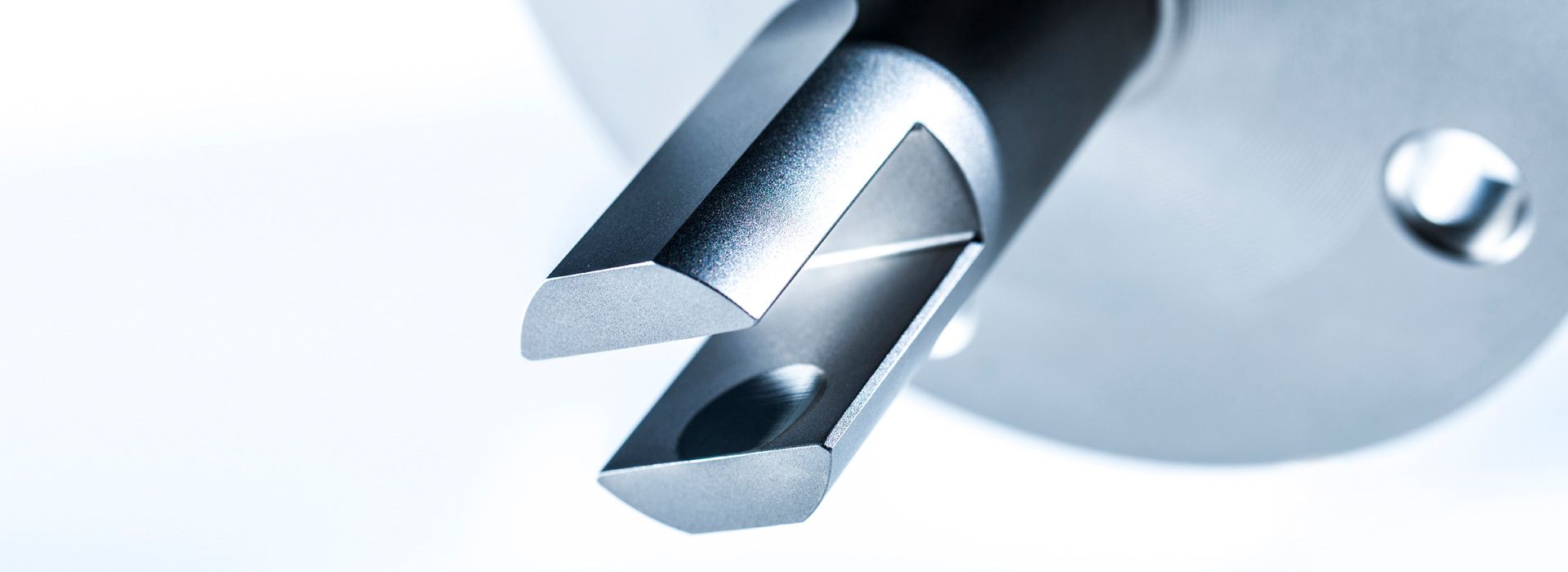
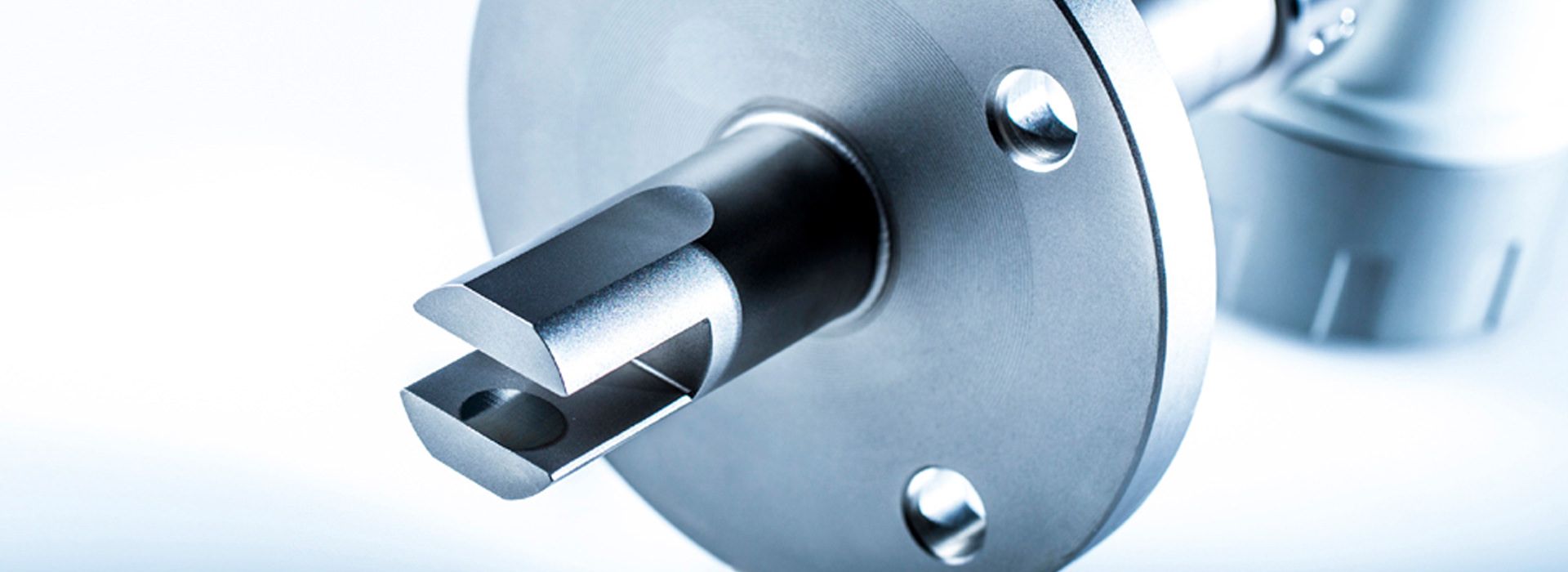
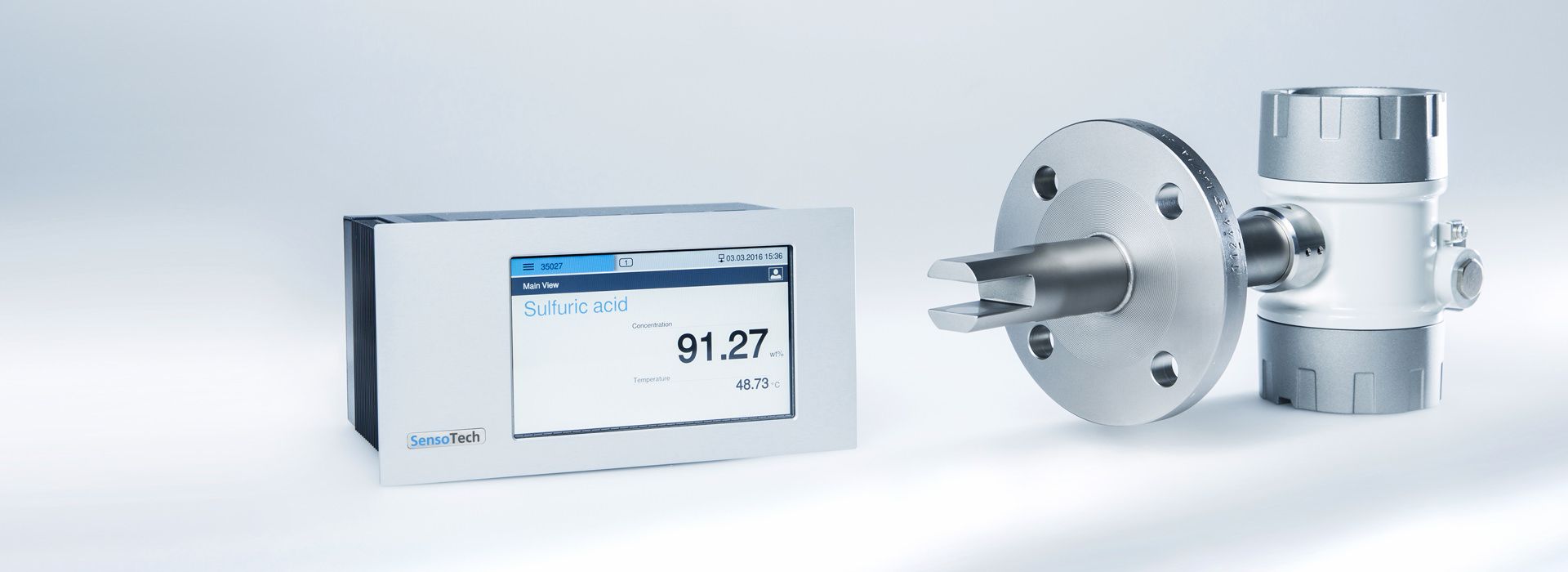
The LiquiSonic® Measuring systems enable inline concentration measurements of acids. The measurement technology can analyze the components of mixtures and can provide information about the concentration or density in real-time. The sensors are based on the principle of ultrasonic velocity measurement. They are therefore almost maintenance-free and can reliably provide measurement values even under demanding conditions.
Measurement methods of LiquiSonic® for determining the concentration of acids
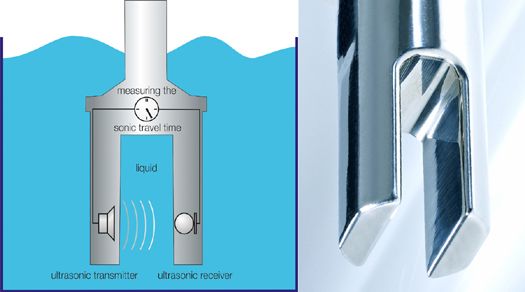
Our LiquiSonic® Measuring systems are based on the principle of sound velocity measurement and are used in various applications to measure the concentration of different acids.
To determine the sound velocity, a sound pulse is sent through the liquid and the time is measured until the pulse reaches the receiver. Since the distance between the ultrasonic transmitter and receiver is constant by design, the sound velocity can be calculated.
Installation of LiquiSonic® Measuring systems
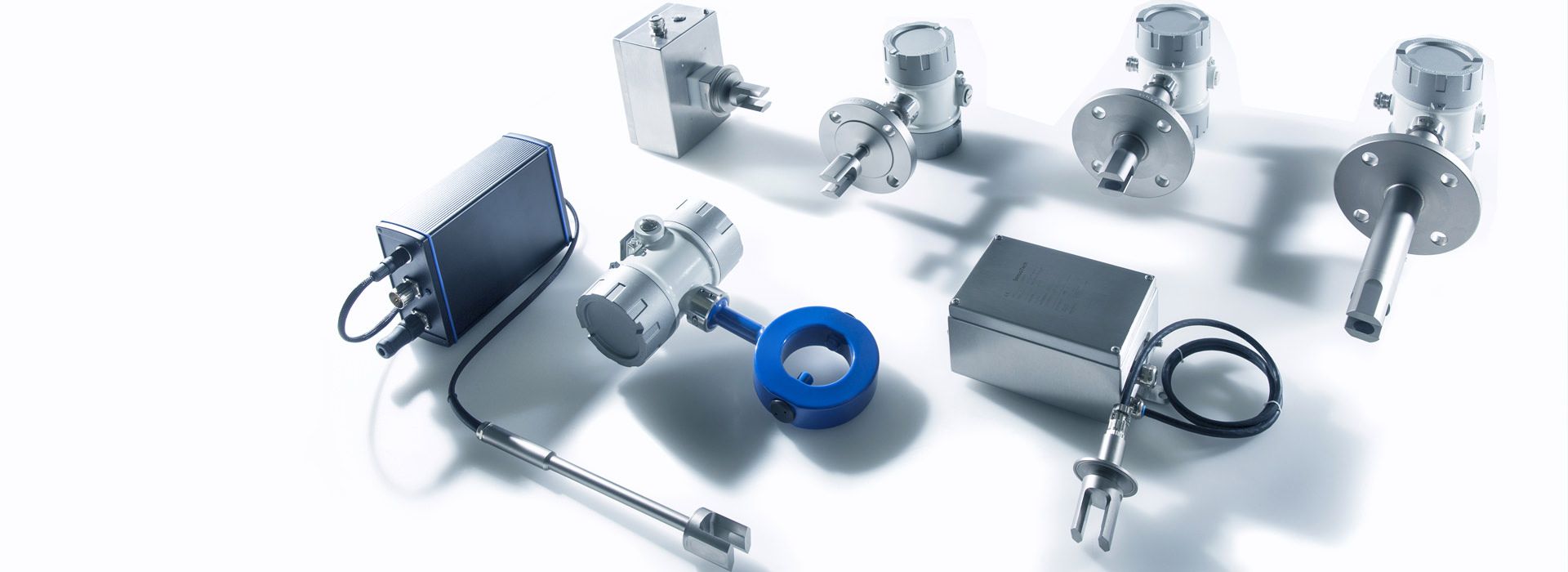
The LiquiSonic® Sensors can be installed directly without a bypass into the user's system, for example in pipelines. There are also different variants tailored to specific applications and have special properties.
What is an acid?
Acids are chemical compounds that can release hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution. The acidity is measured in the unit of pH value, which has a scale from 0 to 14. At a pH value of 7, the solution is neutral and contains equal amounts of H+ ions and OH- ions. Values below 7 indicate acidic character, while values above 7 indicate basic character.
Most acids are soluble in water and can be corrosive or caustic depending on the concentration. An example of an acid is hydrochloric acid, which is widely used in industry and laboratories. It is important to be aware of the properties and effects of acids to handle these substances safely and effectively.
Which liquids can be measured?
As important components in numerous production processes, acids must be regularly tested to ensure their efficiency and quality. Various methods can be used to test or improve specific properties.
One of the most commonly used acids is Hydrochloric acid (HCl), which is used for cleaning pipes and tanks. Sulfuric acid (H2SO4), a strong acid, is often used to lower pH levels or as a cleaning agent for stainless steel. Other common acids are Nitric acid (HNO3), Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) and Hydrofluoric acid (HF), each of which has its specific applications. The choice of the right acid for the testing process depends on the type of liquid and the goals of the test. The correct application of acids helps to increase the efficiency and quality of process liquids and ultimately improve the quality of the final product.

How is the concentration of an acid determined?
The concentration of acids can be determined in various ways. Some common methods are:
- Sound velocity measurement: This method is based on measuring the speed at which sound waves travel through an acid solution. It is particularly suitable for acids with different molecular sizes and structures, as the sound velocity is influenced by these factors.
- Titration: In titration, the acid to be examined is mixed with a base of known concentration until a neutralization point is reached. This method is ideal for precise measurements but unsuitable for acids that do not fully react with the base or where side reactions occur.
- pH MeasurementThis method measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution to determine the acidity. It is effective in aqueous solutions but unreliable for very strong acids or in the presence of other ions that can affect the pH meter.
- Conductivity MeasurementHere, the electrical conductivity of the acid solution is measured, which depends on the ion concentration. This method is useful for ionic acids, but inaccurate for non-ionic or weak acids, as their ions do not contribute sufficiently to conductivity.
- SpectroscopySpectroscopic methods, such as UV-Vis spectroscopy, measure the absorption or emission of light in an acid solution. This is suitable for acids that absorb specific wavelengths but not suitable for acids without characteristic absorption bands.
- Density MeasurementThe density of an acid solution can provide information about its concentration. This is particularly effective for pure acids or solutions with known solvents, but problematic for mixed solutions or when the density is influenced by other dissolved substances.
A classical method is titration, where a base with known concentration is added to the sample until a neutralization point is reached. This method is often used in laboratories to determine the exact molarity of an acid. The advantages of titration are its high precision and reliability, while the disadvantages include the need for skilled operators and time-consuming execution.
Another common method is pH metry, where the pH value of a solution is measured with a pH meter. This method is often used in industrial processes to monitor acid concentration in real-time. Advantages of pH metry include quick and easy handling as well as the possibility of continuous measurement. A disadvantage can be the need for regular calibration and maintenance of the pH meter.
Finally, there are spectroscopic methods such as UV/VIS spectroscopy, which are based on the absorption of light of certain wavelengths by acid molecules. This method is used in research and development to determine the concentration of acids in complex mixtures. Spectroscopic methods score with their ability to detect even very low concentrations, but they are significantly more demanding in terms of the required equipment and know-how.
Applications of concentration measurements of acids
In the chemical industry, concentration measurements of acids played a crucial role in a variety of areas and applications. These measurements are of great importance for quality assurance and process control in various industries such as fertilizer production, the petrochemical industry, the pharmaceutical industry, the food industry, water treatment and environmental protection, battery manufacturing, as well as metallurgy and ore processing.
The concentration measurements of acids make it possible to monitor the progress of chemical reactions, ensure product quality, and ensure that the manufactured products meet the required specifications. In the production of fertilizers, for example, the precise measurement of acid concentration is crucial to ensure that the right nutrients are present in the right amounts. In the petrochemical industry, such measurements help to monitor the effectiveness of catalysts and ensure product purity.
In pharmacy, concentration measurements of acids are indispensable. They make it possible to check the effectiveness of medications and ensure that the correct dosage is administered. In the food industry, such measurements help with quality assurance and control of the acid content in various products. In water treatment and environmental protection, concentration measurements of acids are important to monitor pollution and ensure water quality.
In battery manufacturing as well as metallurgy and ore processing, concentration measurements of acids are used to monitor the composition of materials and optimize process efficiency.
Overall, concentration measurements of acids are of fundamental importance to ensure product quality, process efficiency, and environmental safety in a variety of applications and industries.
Where is the concentration measurement of acids carried out?
In various manufacturing processes, the concentration measurement of acids plays an important role. In particular, pipelines are a critical point, as too high a concentration of acids can damage the pipes and lead to leaks. In addition, unwanted chemical reactions can be triggered, affecting both the quality of the end product and the safety of employees.
For this reason, regular monitoring of acid concentration through precise real-time measurements is indispensable. Various measurement methods, such as pH measurement or ion-selective measurement (ISE), are used. Concentration measurement is carried out not only in pipelines but also at other critical points in the process, such as in tanks or reactors.